New Hope for Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Living with a chronic illness like type 1 diabetes can be challenging. Managing blood sugar requires constant attention. But recent advances bring hope to those dealing with this condition.
In a groundbreaking achievement, scientists in China reprogrammed a woman’s own fat cells to work as insulin-producing cells.
This approach allowed her body to make insulin naturally, without injections. A year later, she still does not need insulin shots.
This success has created hope that reprogramming cells might lead to new ways to treat or even cure type 1 diabetes.
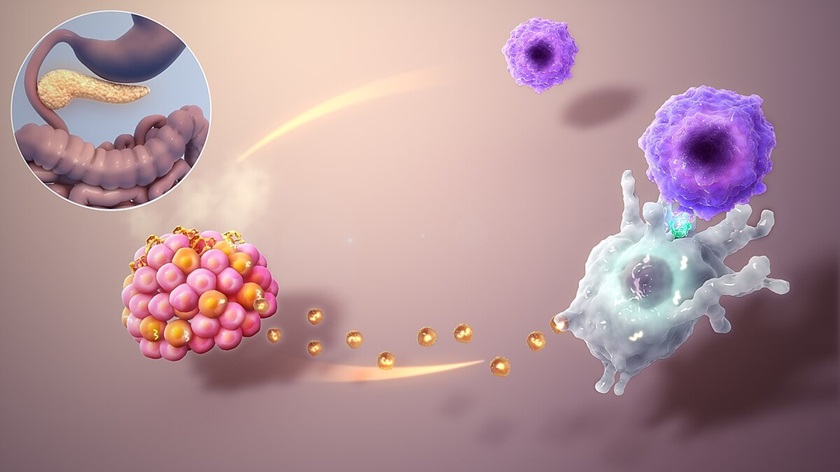
Normally, people with type 1 diabetes rely on daily insulin. Their immune systems attack cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, causing high blood sugar.
But in this study, researchers took fat cells from a patient and turned them into special “pluripotent” stem cells.
These cells can transform into almost any type of cell.
The scientists then turned these stem cells into islet cells, which produce insulin. They placed these cells in the woman’s abdomen, where they began to produce insulin.
Just 75 days after receiving the implant, the woman no longer needed insulin injections. Though transplanting islet cells has been done before, it typically uses cells from donors. This approach is limited because donor cells are scarce.
Only patients who need other transplants, like a kidney or liver, usually get donor islet cells. They also have to take strong immune-suppressing drugs to prevent their bodies from rejecting the new cells.
In this case, the patient had already had a liver transplant, so she was taking immune-suppressing drugs.
But using her own cells for insulin production is a major step forward. The study shows that stem cell-derived cells could potentially reverse type 1 diabetes, even if only for a time.
Other companies, like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, are also exploring stem cell therapies. They use cells from embryos to create islets, which have shown promise in managing blood sugar.
However, one issue remains: the immune system could still attack these transplanted cells.
To make this treatment work for more people, scientists need to find a way to protect these cells without relying on strong immune-suppressing drugs.
This study is a big step toward more effective and natural treatments for type 1 diabetes.
Image Credit: Manu5, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Source: http://www.scientificanimations.com/wiki-images/
You may also like
Image Reference: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Type_1_Diabetes_Mellitus.jpg
Recent Posts
- Social Intelligence: Connecting with confidenceSocial intelligence focuses on reading people, responding with care, and building trust.
- Credit card fraud: How to stay smart and secureMany customers try to increase their credit card limit to enhance their purchasing power.
- SBI opens applications for Specialist Cadre PostsSBI will follow a structured selection process for these vacancies.
- Social Intelligence: Connecting with confidence
What’s new at WeRIndia.com
News from 700+ sources
-
Sara Khan ties the knot with Krish Pathak in Muslim and Hindu rituals, see first photos: ‘Qubool Hai Se Saat Phere Tak’
-
BJP releases chargesheet as Congress completes 2 yrs in Telangana
-
Salem district exceeds target fixed for Armed Forces Flag Day fund: Collector
-
‘I Feel The Pain Of Customers’: IndiGo CEO Confident Of Strong Recovery From Week-Long Crisis
-
Kerala local body elections: 22.54 lakh voters to exercise franchise in Kollam
-
Premises of mini-Vidhana Soudha in Mangaluru cleaned
-
WeRIndia – A News Aggregator
Visit werindia.com for all types of National | Business | World | Politics | Entertainment | Health related news and much more..










Leave a Reply