New Delhi Declaration: Highlights of G20 Summit
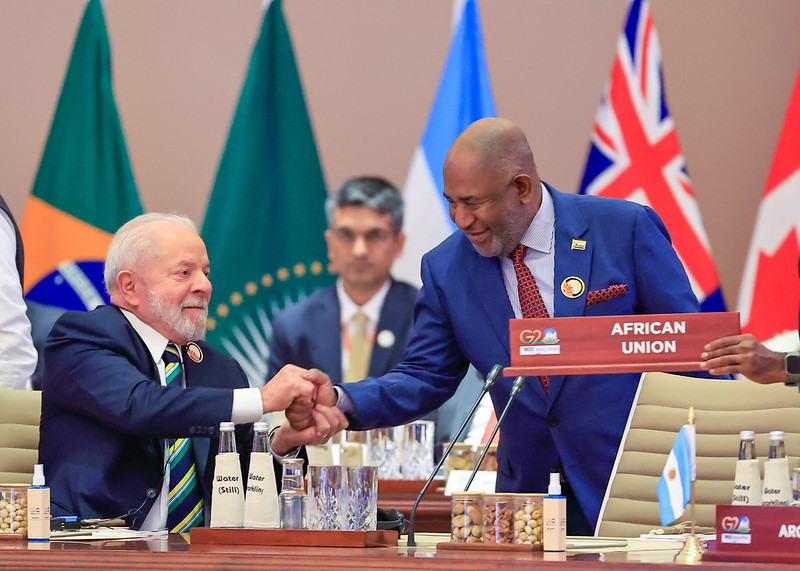

In a significant diplomatic feat, the New Delhi Declaration was unanimously adopted on Saturday by delegates representing the world’s leading economies. Despite their varying positions on critical issues like the Ukraine conflict and climate change, these were approved by them unanimously.
This 37-page document holds several noteworthy highlights:
The declaration refrained from condemning Russia for its involvement in the Ukraine war but urged all nations to abstain from using force to acquire territory.
It emphasized adherence to the principles outlined in the UN Charter and categorically deemed the use or threat of nuclear weapons as ‘inadmissible.’
Additionally, the document called upon both Russia and Ukraine to ensure the swift and unimpeded delivery of essential supplies. These include grains and fertilizers, to meet the needs of developing and least-developed nations, particularly those in Africa.
It also stressed the imperative to halt military attacks on food and energy infrastructure while expressing concerns about the volatility in food and energy markets.
In a significant move towards environmental sustainability, member nations committed to a phasedown of coal, aligning with their respective national circumstances.
Even with major fossil fuel producers like Saudi Arabia, Russia, and Australia, along with coal-reliant nations such as India and South Africa, at the table, the G20 pledged to triple renewable energy sources by 2030.
Addressing climate change financing, the declaration recognized the requirement for developing countries to secure $5.8 to $5.9 trillion before 2030 to achieve their climate objectives.
Furthermore, the world must attract an additional $4 trillion annually by 2030 to work toward the goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
The New Delhi Declaration also emphasized the need for reforming international financial institutions and other things like the commencement of exchanging tax-related information on cryptocurrency assets by 2027.
In matters of monetary policy, the document underscored the commitment of central banks to maintain price stability according to their respective mandates.
It highlighted concerns about tightening global financial conditions, heightened inflation, geo-economic tensions, and the potential exacerbation of debt vulnerabilities.
As such, it reiterated the necessity for well-calibrated monetary, fiscal, and structural policies to promote economic growth and reduce inequalities. It also highlighted the need to sustain macroeconomic and financial stability.
Lastly, the declaration welcomed the African Union as a member of the Group of 20, marking an inclusive step towards addressing global challenges.
The New Delhi Declaration serves as a testament to international cooperation, where nations with differing viewpoints have come together to address critical issues facing the world today.
Image Credit: Palácio do Planalto, CC BY 2.0, Flickr
Image Reference: https://www.flickr.com/photos/palaciodoplanalto/53174519939/in/photostream/









Leave a Reply