Glucometer: What It is and How to Use It
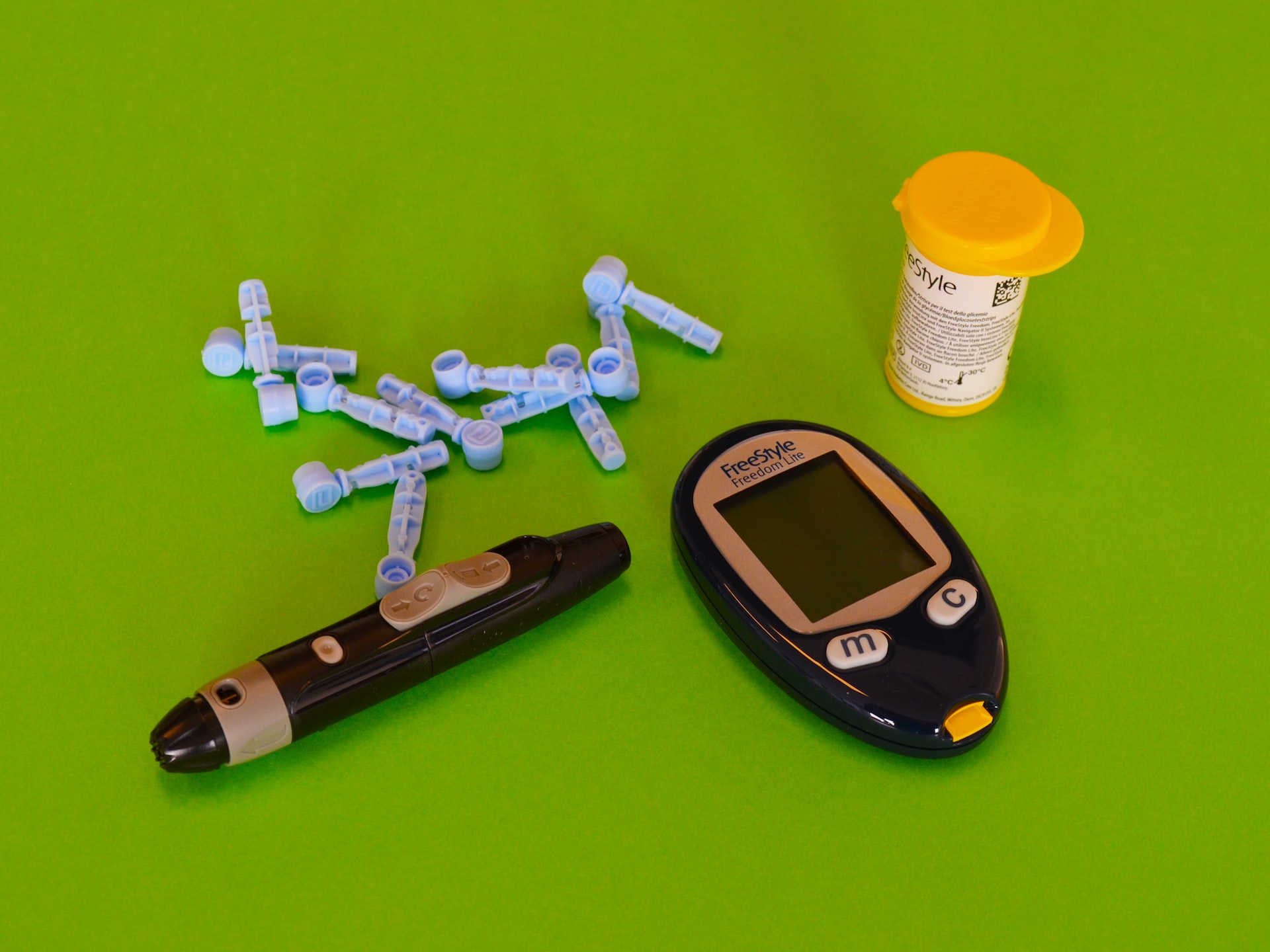
An essential part of self-care for individuals with diabetes is to monitor blood sugar levels and to keep them within a stable range for long-term well-being. Doctors usually measure blood sugar levels using a device called a glucometer. It is important for people with diabetes to test their blood sugar levels regularly, and thus small, portable models of this device can also be used at home. This blog will examine the basics, working principles, procedures and small challenges concerning this machine for sugar test.
What is a Glucometer?
A glucometer is a medical device used to measure blood sugar levels. It is a small, handheld device that uses a drop of blood from a finger prick to measure the amount of sugar in the blood. People with diabetes use glucometers to manage their condition.
Random blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day, and people with diabetes need to be able to monitor their levels and take action if they get too high or too low. Glucometers allow people to do this quickly and easily at home. It can also be used to check for diabetes reversal.
There are different types of glucometers available, and each one works slightly differently.
Some require strips that need to be inserted into the device, while others use sensors that can be placed on the skin. Glucometers are generally accurate, but some factors can affect the accuracy of readings. These include using expired test strips, not following the manufacturer’s instructions, or having very low or very high blood sugar levels.
Before using a glucometer to manage diabetes, it’s important to understand how it works and how to use it properly.
Three Working Principles of Glucometer
As mentioned, this machine for sugar tests follows a simple mechanism. Furthermore, it is also accurate in most cases. But how does a machine measure glucose levels from the blood with such precision? Let’s examine the three main working principles of a glucometer:
- The electrochemical principle: This principle relies on the fact that glucose is an electrolyte and can conduct electricity. When a drop of blood is placed on the electrode, the electrical current will be proportional to the concentration of glucose in the sample.
- The optical principle: This principle uses light to measure the amount of glucose in a sample. A beam of light is passed through the sample and the intensity of the light that passes through is proportional to the concentration of glucose. Hence, in principle, light is the major transmitter in this machine.
- The enzymatic principle: This principle uses enzymes to convert glucose into another substance that can be measured chemically. For example, some glucometers use enzymes to convert glucose into oxygen, which can then be measured with a sensor that detects oxygen levels.
5 Steps to Use a Glucometer
If you have diabetes, it is vital to have a glucometer at hand to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. On a more positive note, it can help keep track of a sugar-free, whole-food diet and see if a reversal of diabetes is possible. However, it is first necessary to understand how to use this device. Here are five steps to using a glucometer:
- Wash hands with soap and water. This will help to prevent infection on both the hands as well as the device.
- Next, use the lancet, the sharp pricking device on the finger to draw a drop or two of blood.
- This drop of blood is then applied to the test strip.
- Alternatively, you can attach it to the glucometer and turn on the device. Once on, gently place a drop of blood on the narrow part of the strip which contains the sensor.
- Wait for the results. The amount of time will vary depending on the type of glucometer being used. However, the general rule of thumb is to wait for at least 5 seconds.
- The readings are mostly displayed in in g/l (grams/litre), mg/dl (milligram/decilitre), or mmol/l (millimoles/litre)
- Record the results in a log book or on a computer. This will help you track your general blood sugar trend as either high, low, or stable across a period of three or more months. The trend will inform you about diabetes reversal.
Precautions You Should Take
There are a few things you should avoid when using a glucometer. First, never reuse test strips. This can lead to inaccurate readings and can potentially damage the glucometer. Second, always make sure that your hands are clean before using the glucometer. Dirty hands can lead to contaminated test strips and inaccurate readings. Finally, avoid eating or drinking anything for at least 30 minutes before taking a reading as they can affect blood sugar levels and give an inaccurate reading. Follow these preventive tips along with the procedures stated above to accurately use this machine for sugar tests.
In All, a Convenient Essential
A glucometer is a handy tool that can help keep track of blood sugar levels across short and long time frames. It can work according to various principles ranging from electrochemical and optic to even enzymatic. Moreover, there are many portable, easy-to-use varieties available in the market today. However, it’s important to use it properly and to be aware of any potential challenges that could occur. Hopefully, this article has helped provide the right information about the judicious usage of a glucometer without encountering any errors or at least keeping them to a minimum.
Image Credit: Photo by Diabetesmagazijn.nl on Unsplash (Source)
Image Reference: Unsplash








Leave a Reply